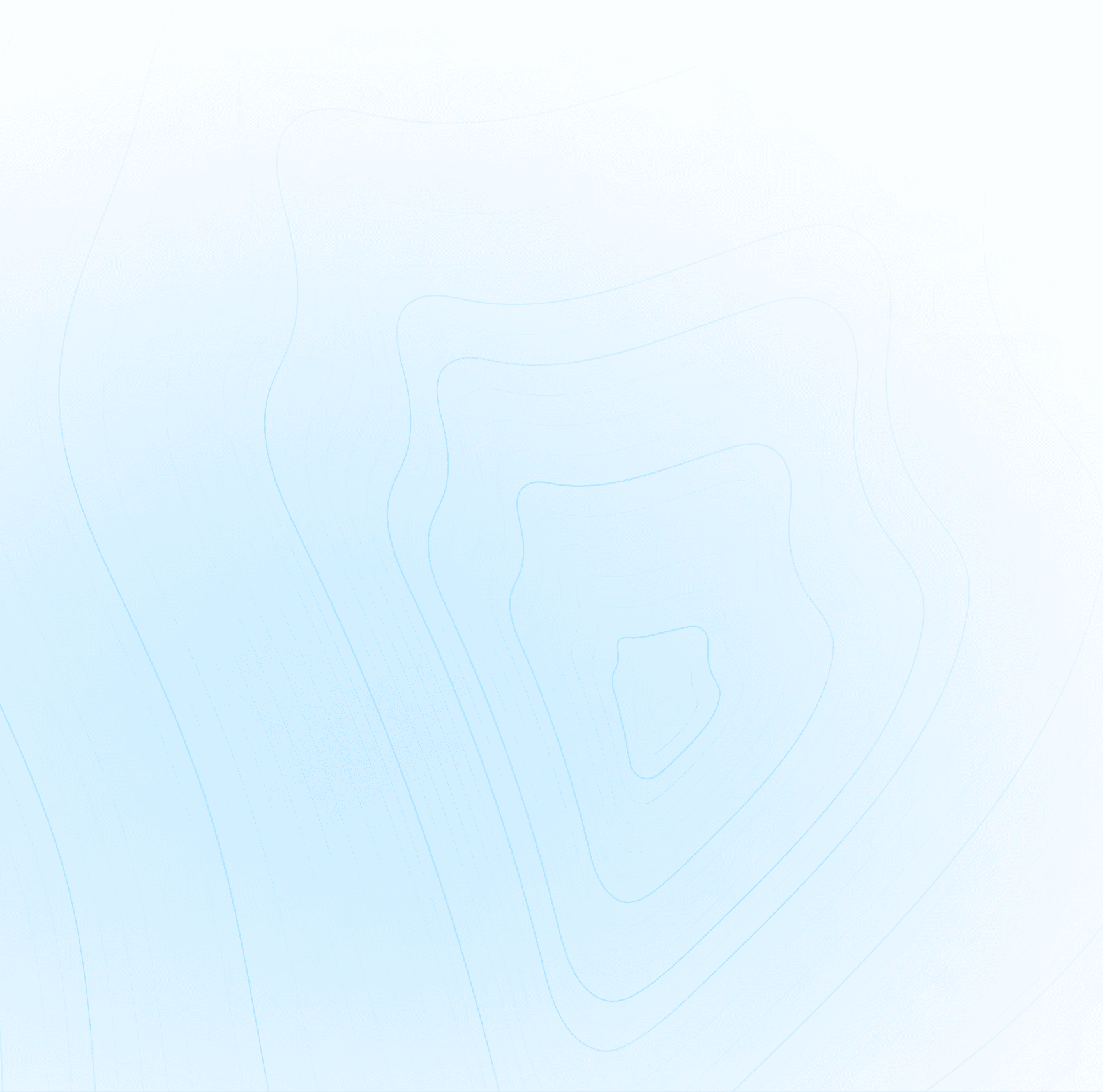Mobile hotspots are portable wireless networks that create internet connectivity using cellular data, featuring configurable security settings, encryption protocols, password protection, and network management capabilities that determine overall connection safety and data protection levels.
The security vulnerabilities of mobile hotspots, default configuration risks, proper setup techniques for maximum protection, implementation best practices that most users overlook, and methods to prevent data breaches while maintaining connectivity independence, are explored in this post, below.
Key Takeaways
-
Mobile hotspots are more secure than public Wi-Fi, offering WPA2/WPA3 encryption and password-protected connections.
-
Major security risks include data interception, man-in-the-middle attacks, rogue networks, and malware spread through compromised devices.
-
Use VPN encryption, strong passwords, and avoid connecting to suspicious or unknown hotspot networks for protection.
-
Change default SSID names, disable broadcast visibility, and regularly update hotspot device firmware and security patches.
-
Monitor connected devices, set connection limits, enable automatic disconnection timers, and conduct monthly security audits.
How Does Mobile Hotspot work?
Mobile hotspots convert cellular network data into Wi-Fi signals that other devices can connect to within approximately 10 meters range.
The cellular radio module receives data transmissions from mobile network towers, which the internal processor converts from cellular data protocols to Wi-Fi compatible formats. This conversion process creates a local wireless network that broadcasts the cellular connection as accessible Wi-Fi.
The bidirectional conversion technology enables simultaneous data flow in both directions - translating incoming Wi-Fi signals from connected devices back to cellular format while maintaining continuous network connectivity. Device compatibility requires Wi-Fi capability on client devices and matching security protocols between the hotspot and connecting devices.
Modern smartphones include built-in hotspot functionality through dedicated software that activates the signal conversion process. This allows users to share their cellular data connection across multiple devices including laptops, tablets, and other Wi-Fi-enabled electronics. The hotspot creates a password-protected network that functions as a portable internet access point, drawing power from the host device's battery while utilizing its existing cellular data plan. Advanced encryption provides an additional security layer that protects data transmitted through mobile hotspot connections from potential interception. Unlike proxy servers that only change IP addresses, VPN protection adds encryption to secure all data transmitted through the mobile hotspot connection.
However, mobile hotspots can still be vulnerable to security threats, as hackers may utilize software to spy on internet traffic and capture sensitive information transmitted over these wireless connections.
public wi-fi vs mobile hotspot security comparison
Types of Mobile Hotspots: Smartphone vs. Portable Wi-Fi Device
Portable Wi-Fi devices support 30–32 simultaneous connections compared to smartphones' 10-device limitation, but cost $75–$650 upfront and require separate data plans.
-
These dedicated connectivity solutions feature advanced cellular modems that enable enhanced signal reception and higher throughput capabilities.
-
5G-enabled portable hotspot models support multiple frequency bands, delivering superior technical specifications for organizations requiring robust wireless connectivity.
The substantial upfront hardware investment ranges from $75 for basic models to $650 for enterprise-grade units. Beyond initial costs, portable Wi-Fi devices require mandatory separate data plan subscriptions, creating ongoing operational expenses.
Organizations must evaluate their specific connectivity requirements — including number of simultaneous users, data throughput needs, and coverage areas — against these cost structures when determining optimal hotspot deployment strategies for secure connectivity initiatives.
Mobile hotspots create public Wi-Fi environments that expose connected devices to potential security vulnerabilities without proper protection measures.
For enhanced security when using mobile hotspots, organizations should consider implementing VPN encryption to protect all internet traffic flowing through these wireless connections from potential monitoring or interception. Since ISPs can monitor network traffic and connected device activity, selecting reputable VPN providers with strong encryption becomes essential for maintaining privacy on mobile hotspot connections.
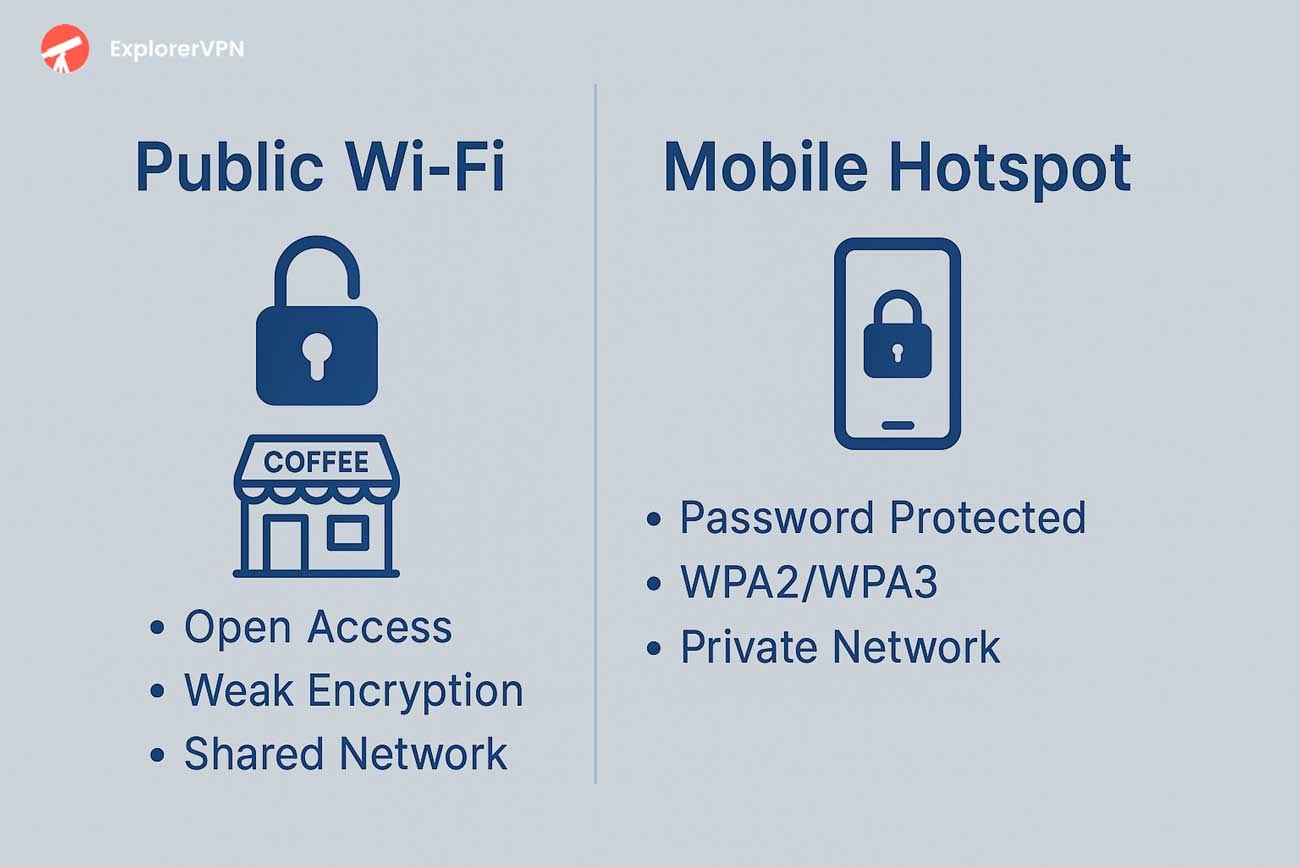
risks when using hotspot
Why Mobile Hotspot Security Matters
Mobile hotspot security vulnerabilities include data breach risks, regulatory compliance failures, network impersonation attacks, and cellular data exploitation that compromise organizational infrastructure and expose sensitive information to cybercriminals.
Data breach prevention represents the primary concern as unsecured mobile hotspot connections enable hackers to intercept sensitive business communications and financial transactions. Organizations face immediate exposure when employees connect through unprotected networks, allowing cybercriminals to capture confidential corporate data and personally identifiable information.
Regulatory compliance requirements mandate that financial institutions implement WPA2 encryption standards to meet data protection obligations. Non-compliance with these security protocols results in regulatory penalties and potential legal liability for organizations handling sensitive financial data.
Network impersonation attacks occur when cybercriminals create fake hotspots using legitimate business names to capture user credentials and authentication information. These sophisticated social engineering tactics target employees who unknowingly connect to malicious networks, compromising corporate security systems.
Cellular data exploitation through unauthorized access leads to excessive bandwidth consumption and unexpected operational costs. Attackers utilize compromised hotspot connections to consume data allowances while maintaining persistent access to organizational networks for extended periods. High-speed servers can provide additional security layers while maintaining optimal performance for legitimate business operations. Regular leak testing ensures that security measures remain effective against evolving threats that target mobile connectivity systems.
Mobile hotspot infrastructure security requires comprehensive protection measures addressing evolving threat landscapes that specifically target corporate connectivity systems, employee authentication protocols, and sensitive data transmission channels. Organizations can enhance hotspot security by implementing VPN encryption protocols that create secure tunnels for data transmission and hide internet traffic from potential interceptors on public networks.
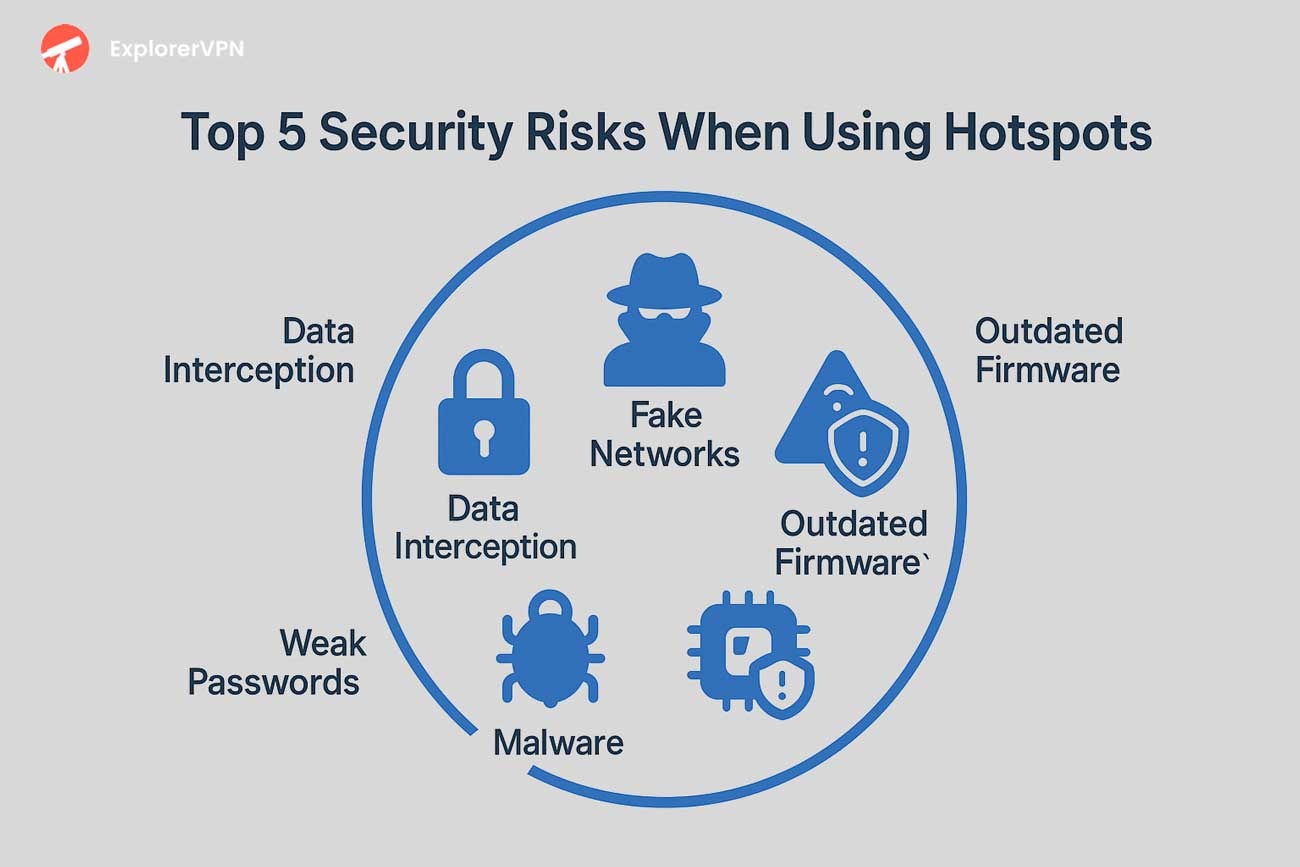
hotspot security toolkit
Common Security Risks When Using Mobile Hotspots
Mobile hotspot security risks include host device vulnerabilities, authentication weaknesses, data interception threats, and rogue network attacks that can compromise entire network infrastructures and expose all connected devices to cyber threats.
Host Device Vulnerabilities
Host device vulnerabilities create the most severe security failures when the device serving as a hotspot is compromised.
-
Malware-infected smartphones or tablets automatically propagate infections to connected laptops, tablets, and other devices.
-
Outdated operating systems lack critical security patches.
-
Jailbroken or rooted devices have disabled built-in security protocols that normally protect against unauthorized access.
Authentication Risks
Authentication risks stem from weak password configurations and outdated encryption methods.
-
Hotspot passwords vulnerable to brute force attacks can be cracked within seconds using automated tools.
-
Default SSID configurations may reveal personal information (like device model or owner name), making targeted attacks easier.
-
Deprecated WEP encryption protocols expose transmitted data to interception, as this encryption can be broken in minutes.
-
Powerful encryption provides essential protection against these vulnerabilities by securing data transmission between devices and access points.
Data Interception Threats
Data interception threats target the wireless transmission between devices and the hotspot.
-
Man-in-the-middle attacks allow attackers to monitor all communications.
-
Packet sniffing tools capture unencrypted data such as passwords, emails, and documents.
-
Session hijacking techniques steal active login sessions, granting unauthorized account access.
-
High-speed servers help maintain performance while preserving security protocols during data transmission.
Shared Connection Environments
Shared connection environments amplify security risks when multiple users connect to the same hotspot.
Uncontrolled activities like downloading infected files or visiting malicious websites can spread malware across all connected devices through shared network resources.
Rogue Network Vulnerabilities
Rogue network vulnerabilities exploit auto-connect features and SSID spoofing techniques.
-
Attackers create fake hotspots with familiar names, automatically connecting devices that joined legitimate networks before.
-
These attacker-controlled networks can intercept all traffic and inject malicious content into browsing sessions.
-
Using a VPN server helps reduce these risks by encrypting all data transmitted through mobile hotspot connections, protecting personal information even on potentially compromised networks.
Is a Mobile Hotspot Safer Than Public Wi-Fi?
Mobile hotspots are safer than public Wi-Fi due to superior encryption protocols, access controls, and cellular network architecture that prevents common attack vectors.
Mobile hotspots provide WPA2/WPA3 encryption standards that significantly outperform the weak or often absent encryption found on public Wi-Fi networks. The password-protected connections create authentication barriers that limit unauthorized device access, while public networks typically allow anyone to connect without verification.
The cellular network architecture inherently reduces susceptibility to man-in-the-middle attacks compared to traditional Wi-Fi infrastructure. Mobile hotspots also feature unique network identification that eliminates the risk of connecting to fraudulent hotspots - a common spoofing technique used by attackers on public networks.
These security advantages stem from the fundamental differences between cellular data transmission and public Wi-Fi broadcasting. Mobile carriers implement carrier-grade security measures and network segmentation that isolate individual connections, while public Wi-Fi networks often lack proper network isolation, allowing potential attackers to monitor traffic from other connected devices.
The controlled access environment of mobile hotspots means only devices with the correct credentials can establish connections, creating a private network bubble that public Wi-Fi cannot match due to its open-access design. High-speed servers in multiple locations can also complement mobile hotspot security by providing additional routing options for users seeking enhanced performance and privacy protection.
For additional protection, users can enhance their mobile hotspot security by using a secure virtual private network that encrypts data and hides their real IP address for enhanced privacy across all connected devices. VPN services provide powerful encryption that adds an extra layer of security to protect against hackers and data breaches on any connection type.
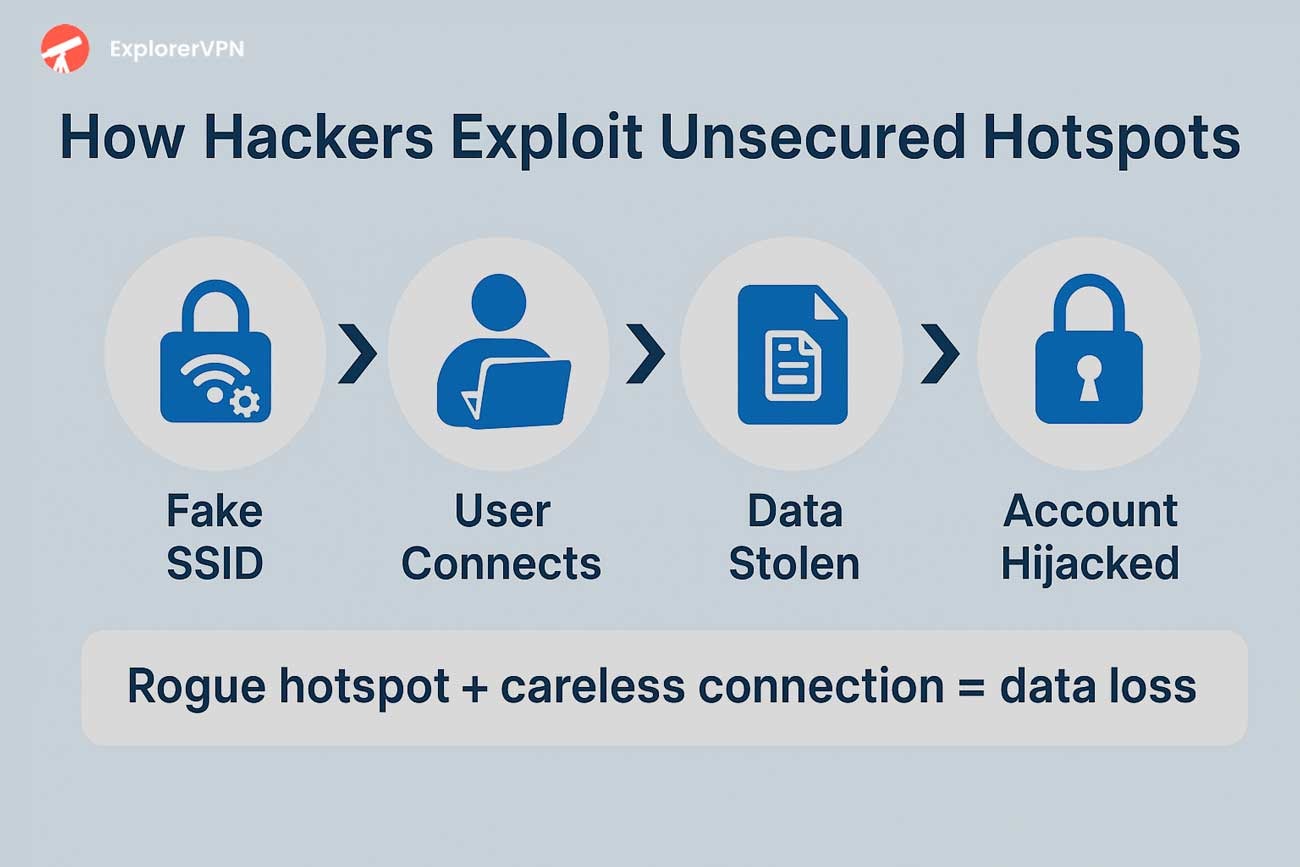
How Hackers Can Exploit Unsecured Hotspots?
Hackers exploit unsecured hotspots through data interception, rogue networks, credential theft, session hijacking, network manipulation, and traffic analysis.
-
Data interception: Cybercriminals use packet sniffing tools to capture unencrypted transmissions, revealing login credentials, passwords, and sensitive personal information transmitted without proper encryption protocols.
-
Rogue hotspots: Attackers impersonate legitimate networks using identical SSIDs (network names) so users unknowingly connect to attacker-controlled infrastructure (e.g., coffee shop or hotel Wi-Fi).
-
Credential theft: Fake websites and SSL stripping force HTTPS to downgrade to HTTP, exposing banking information, email passwords, and social media credentials.
-
Session hijacking: Attackers steal active cookies and authentication tokens from unencrypted traffic, allowing impersonation on sites and apps without original login credentials.
-
Network manipulation: Real-time control over traffic lets attackers inject malicious code, redirect users to fraudulent sites, or modify downloaded files during transmission.
-
Traffic analysis: Continuous monitoring reveals browsing patterns, personal preferences, and behavioral data used to build profiles for targeted attacks or identity theft.
These techniques succeed primarily because of insufficient user awareness about unsecured connection risks and a lack of proper security protocols like VPN usage or connection verification procedures.
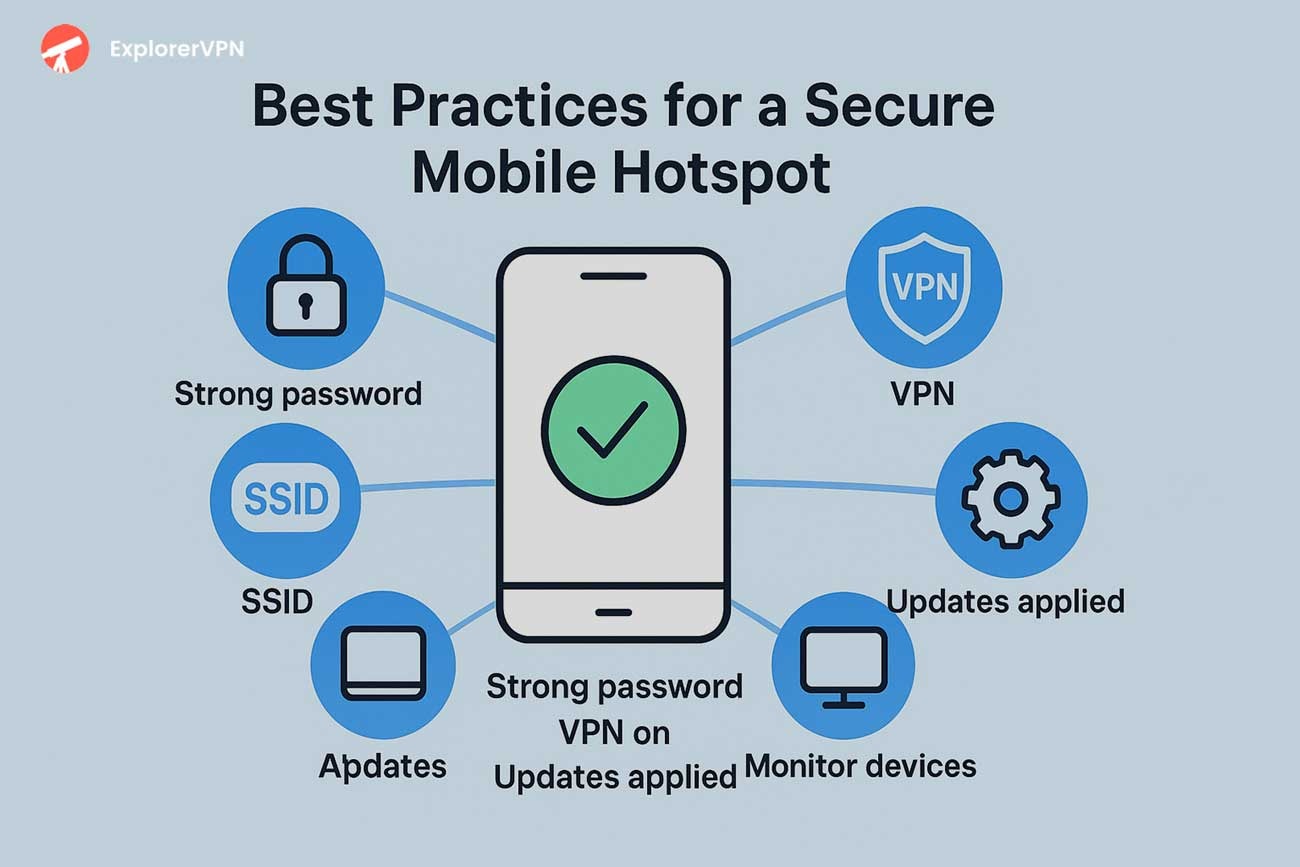
best practices for secure mobile hot spot - strong password, ssid, vpn, updated applied
How to Secure Your Mobile Hotspot?
Mobile hotspot security requires SSID management, strong passwords (minimum 10 characters with mixed case, numbers, symbols), connection monitoring, regular updates, and multi-factor authentication.
SSID management involves changing default network names to non-identifying alternatives and disabling broadcast visibility to reduce attack surface exposure. Password complexity must exceed basic requirements through combinations utilizing uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols while avoiding predictable patterns.
Connection settings configuration includes disabling automatic connections and enabling "forget network" functions after public hotspot sessions to prevent unauthorized reconnection. Device monitoring protocols require regular verification of connected devices and usage tracking for anomaly detection of potential intrusions.
Security updates maintenance involves prompt application of system patches and anti-malware protection to address newly discovered vulnerabilities. Authentication methods enhancement includes multi-factor authentication implementation and data encryption verification through HTTPS connections to protect transmitted information.
Threat assessment requires continuous monitoring of connection speeds and data patterns for unauthorized access indicators, allowing early detection of security breaches or compromised network integrity.
Advanced Protection: Using VPNs and Encryption (WPA2/WPA3)
VPNs and WPA2/WPA3 encryption provide advanced protection through encrypted tunnels, multi-factor authentication, and stronger authentication mechanisms, but may introduce vulnerabilities, latency issues, and streaming service blocks.
VPN protocols like WireGuard create secure encrypted tunnels that protect data transmission across cellular networks while optimizing performance. WPA3 encryption delivers enhanced protection over WPA2 through stronger authentication mechanisms and advanced security layers.
Corporate implementations integrate multi-factor authentication with secure tunneling protocols for comprehensive data protection. These advanced encryption standards establish extensive defense mechanisms against sophisticated cyber threats through layered security approaches.
However, VPN protocols may contain exploitable vulnerabilities requiring multiple security layers rather than singular reliance. Advanced encryption can introduce latency challenges across multiple devices, while streaming services actively block VPN traffic, limiting accessibility through encrypted channels. These limitations necessitate careful consideration when implementing advanced protection measures.

signs your hotspot is compromised
How to Manage and Monitor Connected Devices
Connection protocols must enforce predetermined device limits and automatic disconnection timers, while monthly audits reveal data-intensive activities and unauthorized access attempts through extensive logging systems.
-
Real-time monitoring systems track connection duration and data consumption patterns across all network endpoints.
Automated alerting mechanisms immediately flag policy violations and unauthorized connection attempts, enabling rapid response to security threats. -
Security posture verification acts as a critical gateway, requiring current patches and compliant configurations before allowing network access.
This prevents vulnerable devices from compromising network integrity.
Regular maintenance cycles ensure firmware updates remain current while maintaining documented compliance histories for audit purposes. -
Device limits prevent network overload by restricting the number of simultaneous connections per user or device type.
Automatic disconnection timers terminate inactive sessions, freeing network resources and reducing security exposure from abandoned connections. -
Extensive logging systems capture detailed activity records, enabling administrators to:
-
Identify data-intensive applications
-
Detect unusual usage patterns
-
Trace unauthorized access attempts back to their source
These logs also support forensic analysis and compliance reporting requirements.
-
Network security integrity depends on the systematic implementation of these management components, creating multiple layers of protection while maintaining optimal performance across all connected devices.
How to Detect if Your Hotspot Has Been Compromised?
Compromised hotspot indicators include unexplained data consumption spikes, persistent latency increases, frequent disconnection events, unauthorized MAC addresses, certificate warnings, DNS resolution failures, and suspicious login portal redirects.
Mobile hotspots provide essential connectivity flexibility but expose users to significant security risks when compromised. Data theft, credential harvesting, and unauthorized surveillance activities often remain undetected without proper monitoring protocols.
Network connection anomalies manifest through unrecognized MAC addresses connecting to your hotspot, geographically improbable device locations appearing in logs, and excessive connected device counts beyond your expected users. Monitor your hotspot's administrative interface regularly to identify these unauthorized connections.
Traffic and performance irregularities include certificate warnings when browsing secure websites, DNS resolution failures preventing normal internet access, and automatic redirects to suspicious login portals. These symptoms indicate potential man-in-the-middle attacks or DNS hijacking attempts.
System integrity verification requires checking administrative interface accessibility for unauthorized changes, confirming firmware version consistency against manufacturer updates, and ensuring encryption protocol maintenance. WPA3 or WPA2 encryption should remain active and unchanged from your original configuration.
External security monitoring through intrusion detection systems, credential exposure alerts from security tools, and breach notifications provide additional compromise detection layers. Security software may alert you to suspicious network behavior or credential theft attempts requiring immediate investigation and potential hotspot reset.
Best Practices for Safe Mobile Hotspot Use
Mobile hotspot security requires WPA3 encryption, VPN protection, disabled unnecessary protocols, and connection management controls to protect organizational data transmission effectively.
WPA3 encryption serves as the primary defense mechanism, requiring passwords with 12+ characters incorporating mixed case letters, numbers, and symbols to prevent unauthorized access attempts. This encryption standard provides enhanced protection against brute force attacks and maintains data confidentiality during wireless transmission.
VPN tunneling creates an additional security layer by encrypting all internet traffic through enterprise-grade endpoint protection. This protocol ensures that sensitive organizational data remains protected even when transmitted over potentially compromised networks, establishing secure communication channels between mobile devices and corporate infrastructure.
Protocol management involves disabling file sharing, Bluetooth, LLMNR, and NetBIOS services that create unnecessary attack vectors. These protocols often operate automatically without user awareness, potentially exposing devices to network-based exploits and unauthorized data access attempts.
Connection controls include implementing connection limits to prevent network overload, using anonymous SSID naming to avoid revealing organizational identity, and establishing scheduled password rotation policies to maintain long-term security integrity. These administrative controls ensure sustainable hotspot operations while minimizing security risks through proactive management practices.
Are Hotspots Secure: FAQ’s
How Much Data Does Using a Mobile Hotspot Consume Monthly?
Mobile hotspot data consumption typically ranges from 10-15 GB monthly for average users. Monthly usage varies considerably based on specific user activities, with streaming video dramatically increasing data consumption compared to basic web browsing or email. Mobile carriers enforce specific usage limits and implement throttling thresholds that restrict hotspot functionality once certain data allowances are exceeded, affecting connection speeds and overall performance.
Can Mobile Hotspots Work Internationally When Traveling Abroad?
Yes, mobile hotspots can work internationally when traveling abroad through several connectivity options. Mobile hotspots demonstrate international compatibility through dedicated devices, carrier data roaming add-ons, or local SIM solutions. However, travelers face significant limitations including coverage gaps, speed variations, strict data caps, and elevated security risks requiring methodical mitigation strategies.
What's the Battery Life Difference Between Smartphone and Dedicated Hotspot Devices?
Dedicated hotspot devices provide significantly longer battery life than smartphones used for tethering, with hotspots delivering 6-24 hours of continuous operation compared to smartphones experiencing 20-30% hourly battery depletion. This battery efficiency disparity means dedicated hotspot devices can maintain internet connectivity throughout extended periods without charging, while smartphone tethering rapidly drains the phone's battery and compromises its primary functionality. The continuous operation capability of dedicated hotspots eliminates frequent charging interventions that smartphone users must perform when using their device as a mobile internet source.
Do Mobile Hotspots Slow Down Internet Speed for Connected Devices?
Yes, mobile hotspots do slow down internet speed for connected devices. Mobile hotspots reduce internet speeds through bandwidth division among connected devices, signal degradation from limited cellular tower range, and data throttling constraints from cellular carriers, which compromises connection quality and degrades overall user experience compared to dedicated broadband solutions like fiber or cable internet.
How Many Devices Can Simultaneously Connect to One Mobile Hotspot?
Most mobile hotspots can simultaneously connect 8-10 devices. Mobile hotspot connection limits are constrained by firmware restrictions and hardware capabilities of the smartphone or dedicated hotspot device. Device compatibility and maximum connections vary across wireless carriers like Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile, as well as different smartphone models including iPhone and Android devices. Network performance and data speeds typically degrade as the number of simultaneous connections approaches the maximum theoretical capacity limits, with factors like bandwidth allocation and signal strength affecting overall connectivity quality.