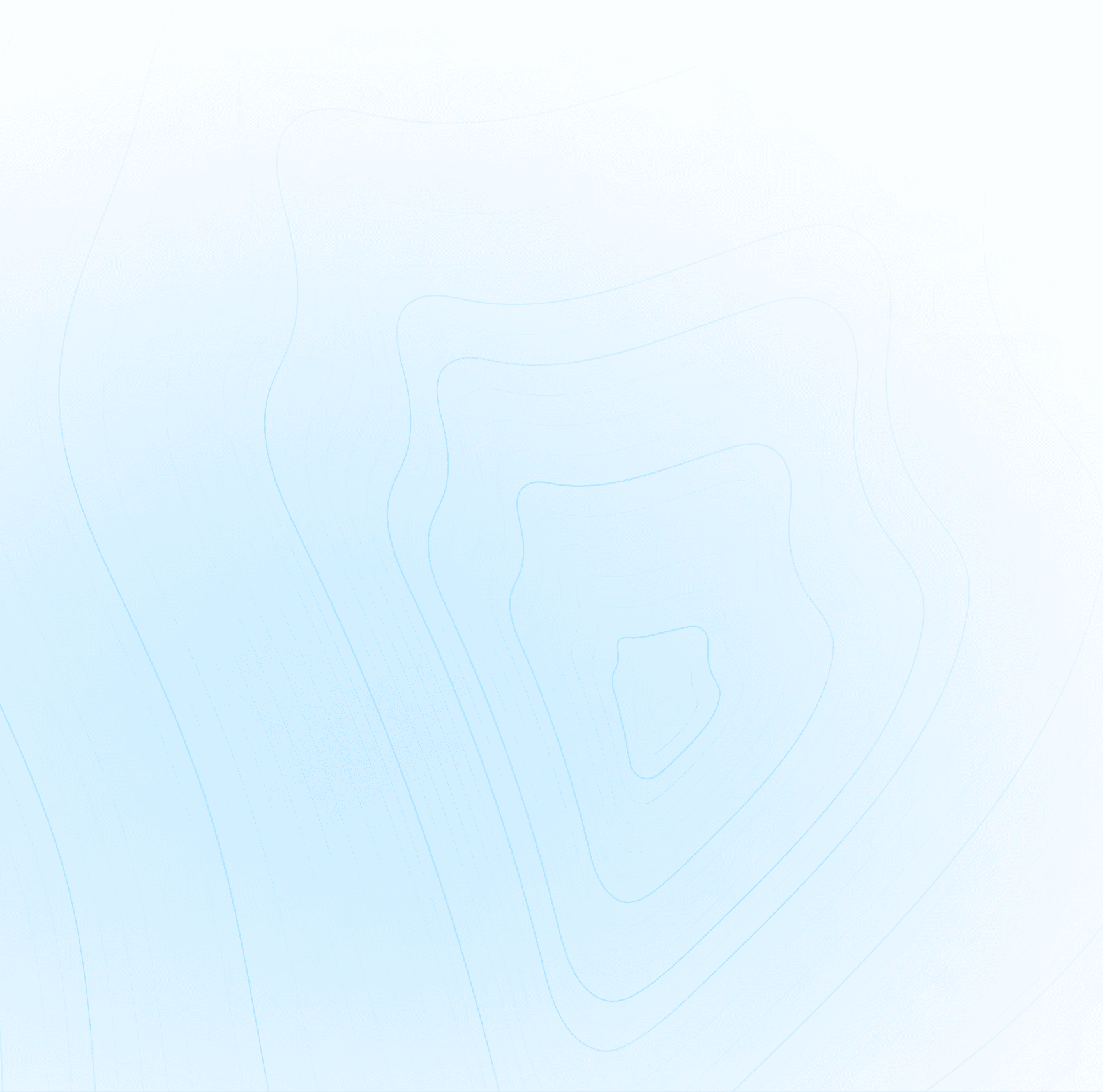A travel router is a portable networking device - one of the most portable and compact devices for travelers that creates secure, encrypted connections and acts as a personal Wi-Fi gateway, protecting multiple devices from cybersecurity threats on public networks and prying eyes, while enabling seamless internet access anywhere.
The escalating cybersecurity risks of public Wi-Fi networks, how travel routers establish encrypted security tunnels, their advantages over standard mobile hotspots, specific vulnerabilities they mitigate including data interception and man-in-the-middle attacks, and why these compact networking devices are essential for modern travelers, is explored in this post, below.
What is travel router
Key Takeaways
-
A travel router is a compact networking device under four inches that creates secure, portable Wi-Fi connections anywhere you go.
-
It provides enhanced security with hardware firewalls, VPN protocols, and WPA3 encryption to protect against public Wi-Fi vulnerabilities.
-
Travel routers bypass device limitations by creating a single connection point that supports multiple devices without per-device fees.
-
Travel routers act as a central hub, managing and distributing internet access to all your devices.
-
They offer versatile operation modes including hotspot conversion, range extension, and access point functionality for seamless connectivity.
-
They help you stay connected by providing a stable connection in hotels, airports, and remote locations.
-
Essential for mobile professionals, travel routers enable stable remote work, geo-restriction bypass, and secure international internet access.
What Is a Travel Router?
A portable travel router, one of the most compact devices for travelers, creates secure, portable Wi-Fi connections by acting as an intermediary between public networks and your personal devices.
These specialized networking appliances measure under four inches and weigh less than six ounces, making them highly portable for global deployment. Travel routers feature integrated Wi-Fi antennas, Ethernet ports for wired connections, and international voltage compatibility to function across different countries and power systems.
The primary advantages include encrypted traffic tunneling, isolated network segmentation, and centralized security protocol implementation across multiple connected endpoints. This architecture prevents direct device exposure to potentially compromised public network infrastructure while maintaining consistent network identity across geographic locations.
Advanced travel router models incorporate cellular failover capabilities, enterprise-grade VPN tunneling, and multi-source internet aggregation. These features enable users to establish reliable, secure connections in environments where standard network access proves inadequate or compromised, such as hotels, airports, cafes, or remote locations. The Slate AX is an example of a compact, Wi-Fi 6-enabled portable travel router. For users requiring maximum privacy protection, some travel routers support Onion Over VPN configurations that combine VPN encryption with Tor network anonymization for enhanced security against surveillance. When using VPN functionality, it’s important to choose travel routers that support no-logs policies to prevent user activity from being recorded and potentially accessed by third parties.
The devices function as intermediary gateways, creating a protective barrier between untrusted public networks and personal smartphones, laptops, tablets, and other devices. The travel router acts as a central hub, managing all devices connected and ensuring consistent security protocols for every device on the network. This ensures all connected devices benefit from the router’s security protocols without requiring individual configuration on each device. Travel routers provide essential protection against evil twin attacks, where malicious actors create fake Wi-Fi hotspots to intercept sensitive data from unsuspecting users on public networks.
how travel router works
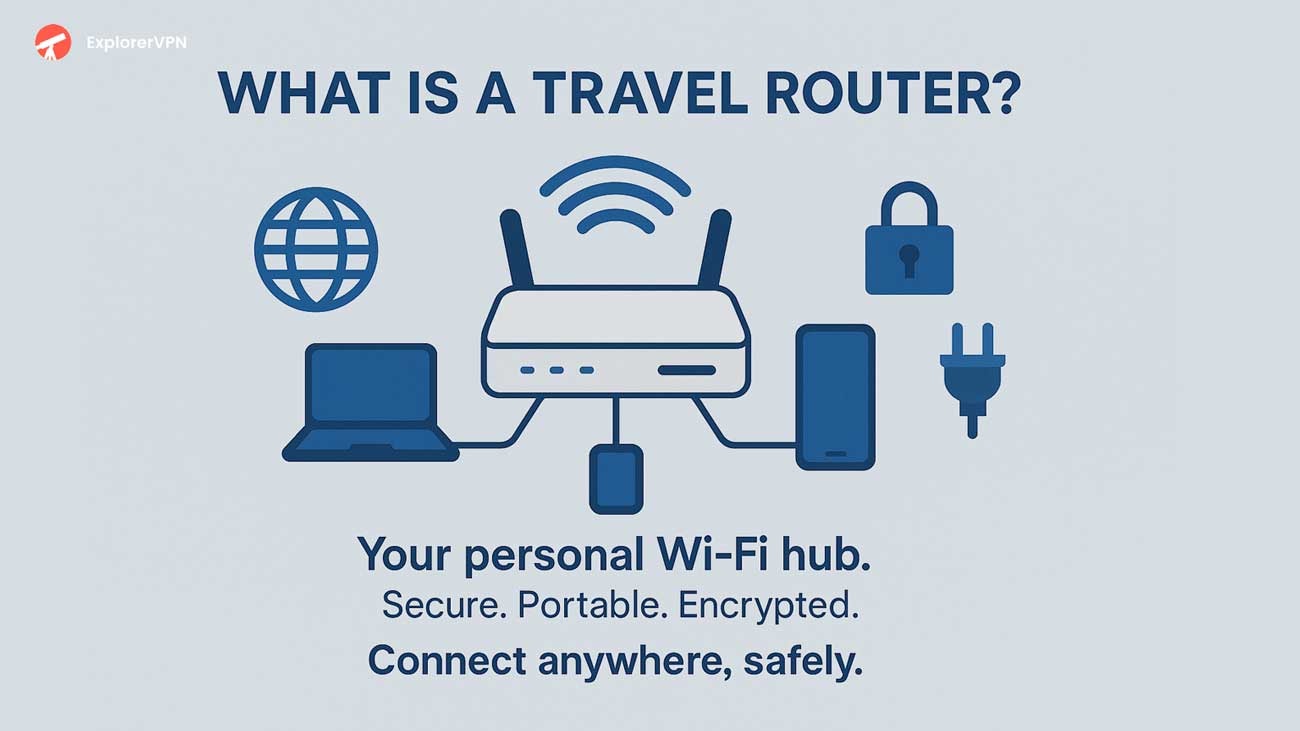
How Does a Travel Router Work?
Travel routers work by creating a portable Wi-Fi network that connects to existing internet sources and redistributes connectivity to multiple devices simultaneously, allowing you to easily connect multiple devices through a single hub.
Connection stability exceeds smartphone tethering capabilities through specialized antenna arrays and persistent authentication token storage. These routers maintain stronger signal reception and transmission compared to mobile hotspots due to their dedicated wireless hardware components.
The system maintains captive portal credentials, automating browser-based login sequences that typically require manual input on hotel or public networks. This eliminates the need to repeatedly enter login information across different devices.
Traffic routing occurs transparently through the device, presenting single-device signatures to source networks while managing multiple downstream connections. The router uses network address translation protocols to mask the actual number of connected devices, making it appear as one user to the host network. This simplifies network management by allowing you to control all devices connected through a single interface, preventing connection limits or additional fees that some networks impose for multiple device usage.
The router’s dual-band capabilities allow simultaneous connection to source networks on one frequency while broadcasting a separate network on another frequency, optimizing bandwidth distribution across connected devices. This enables you to connect to different networks as needed while maintaining a stable connection for all your devices. Many travel routers also support VPN connections, creating an encrypted tunnel that protects all connected devices from potential security threats on public Wi-Fi networks.
Travel routers enhance online security by providing powerful encryption that shields your data from potential threats when accessing public networks in hotels, airports, or cafes. By connecting to an existing Wi Fi network, the travel router creates a private Wi Fi signal for your devices, improving privacy and security. These devices offer global connectivity across multiple regions, ensuring reliable internet access regardless of your travel destination.
Travel Router vs. Hotspot vs. Regular Router
Travel routers provide enhanced security protocols, accept any SIM card (with the right data plan), offer advanced firewall configurations, and create isolated network environments — while mobile hotspots have 4–10 hour battery life and basic security protocols insufficient for public network protection.
-
Travel routers establish encrypted connections when accessing public Wi-Fi infrastructure, creating secure tunnels that protect data transmission from potential threats.
-
These devices operate independently of carrier restrictions, allowing users to insert any compatible SIM card with an appropriate data plan for seamless connectivity.
-
They can also function as Wi-Fi extenders for existing networks.
-
Having your own router enables the creation of a private local area network (LAN), allowing device sharing and local services unavailable on public Wi-Fi hotspots.
Mobile hotspots present operational constraints through limited battery capacity, typically requiring recharging every 4–10 hours of active use. Their basic security implementations lack the sophisticated threat detection and network isolation capabilities needed to protect sensitive data on public networks.
-
Travel routers excel in remote operations with enterprise-level firewall configurations that filter incoming and outgoing traffic, monitor network activity, and block suspicious connections.
-
The network isolation feature creates separate virtual networks, preventing unauthorized access to connected devices and maintaining secure communication channels vital for business and sensitive data handling.
-
Travel routers can also change your IP address to bypass geographic restrictions and access region-blocked content.
For maximum protection, many users configure travel routers to work with VPN services, creating an additional encrypted tunnel that masks the IP address and secures all internet traffic.
Modern travel routers support powerful encryption standards that ensure data remains protected even when connecting through untrusted public networks.
Why Use a Travel Router While Traveling?
Travel routers provide centralized network security, eliminate per-device fees, bypass device restrictions, and enable single-point authentication while protecting against public Wi-Fi vulnerabilities.
A travel router establishes a hardware firewall barrier that isolates your personal devices from shared network threats on untrusted public infrastructure. This configuration enables encrypted VPN transmission protocols and implements DNS-over-HTTPS to protect against eavesdropping attacks and security vulnerabilities.
The router circumvents venue-specific restrictions that typically block gaming consoles and streaming devices while maintaining mDNS protocol support for seamless device interoperability. Instead of configuring Wi-Fi settings on each device separately, travelers benefit from single-point network authentication that eliminates repeated setup across multiple endpoints.
Cost savings occur through avoiding per-device billing structures common on cruise ships and premium hotel networks. The travel router preserves local network communication between smartphones, laptops, and IoT peripherals regardless of location changes, maintaining operational efficiency while traveling. This is especially useful for staying connected during your next trip, ensuring all your devices have reliable access wherever you go. Travel routers paired with VPN services featuring high-speed servers like Atlanta or Frankfurt deliver optimal performance for streaming and video chat applications while abroad.
The centralized network management system addresses the inherent operational inefficiencies of connecting multiple devices directly to public Wi-Fi networks, providing both enhanced security and improved travel convenience through unified network control. Travel routers can also securely share your phone's internet connection with all your devices, making it easier to stay online when Wi-Fi is unavailable. Regular testing with tools like dnsleaktest.com ensures your VPN connections remain secure and leak-free throughout your travels. Modern VPN applications can be downloaded from App Store or Google Play and easily configured with your travel router for enhanced privacy protection.
Key Benefits of a Travel Router
Travel routers provide security enhancement, cost mitigation, device management, and signal optimization benefits.
Security enhancement implements firewall isolation between public networks and personal devices, supporting integrated VPN tunneling with DNS-over-HTTPS and Wireguard protocols for thorough data privacy protection. This creates a secure barrier that prevents unauthorized access to your personal devices when connected to potentially unsafe public Wi-Fi networks in hotels, airports, or cafes. Many travel routers are compatible with VPN server locations in USA and worldwide, allowing users to select optimal connection points for enhanced privacy and access to geo-restricted content. The VPN creates an encrypted tunnel for all traffic passing through the travel router, turning browsing data into unreadable code that protects against hackers and network monitoring. Travel routers with VPN capabilities enable fast, risk-free browsing while maintaining your privacy regardless of your physical location.
Cost mitigation eliminates per-device fees through shared connection architecture while reducing roaming charges via cellular backup functionality. Instead of paying separate connection fees for each device, multiple devices can share a single internet connection, significantly reducing overall connectivity costs during travel.
Device management bypasses network restrictions affecting gaming consoles and streaming devices, enabling mDNS functionality for Chromecast operation. Many hotel and public networks block certain device types or streaming services, but travel routers create a private network that allows all devices to function normally, including gaming systems, smart TVs, and casting devices.
Signal optimization leverages enhanced antenna arrays for superior network stability, extending coverage beyond standard mobile device capabilities while maintaining consistent multi-device performance. The improved antenna design and signal processing provide stronger, more reliable connections that can support multiple devices simultaneously without degrading performance.
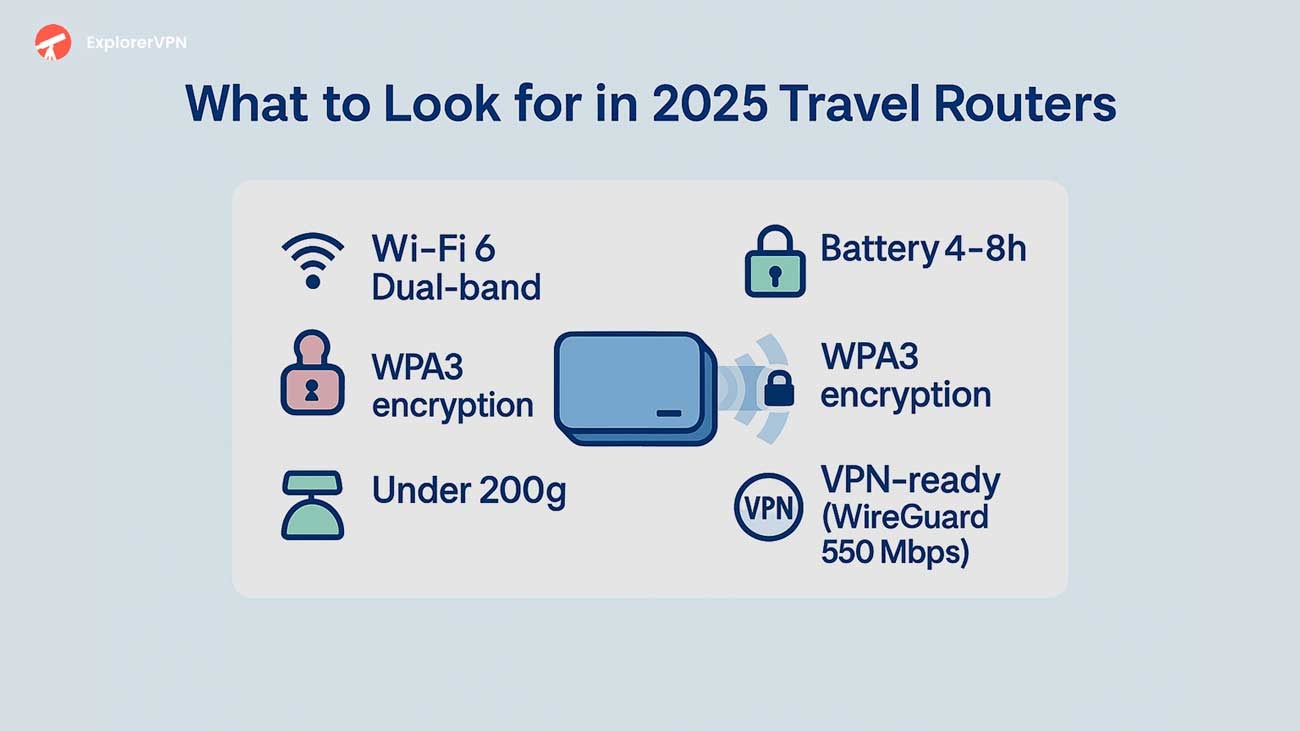
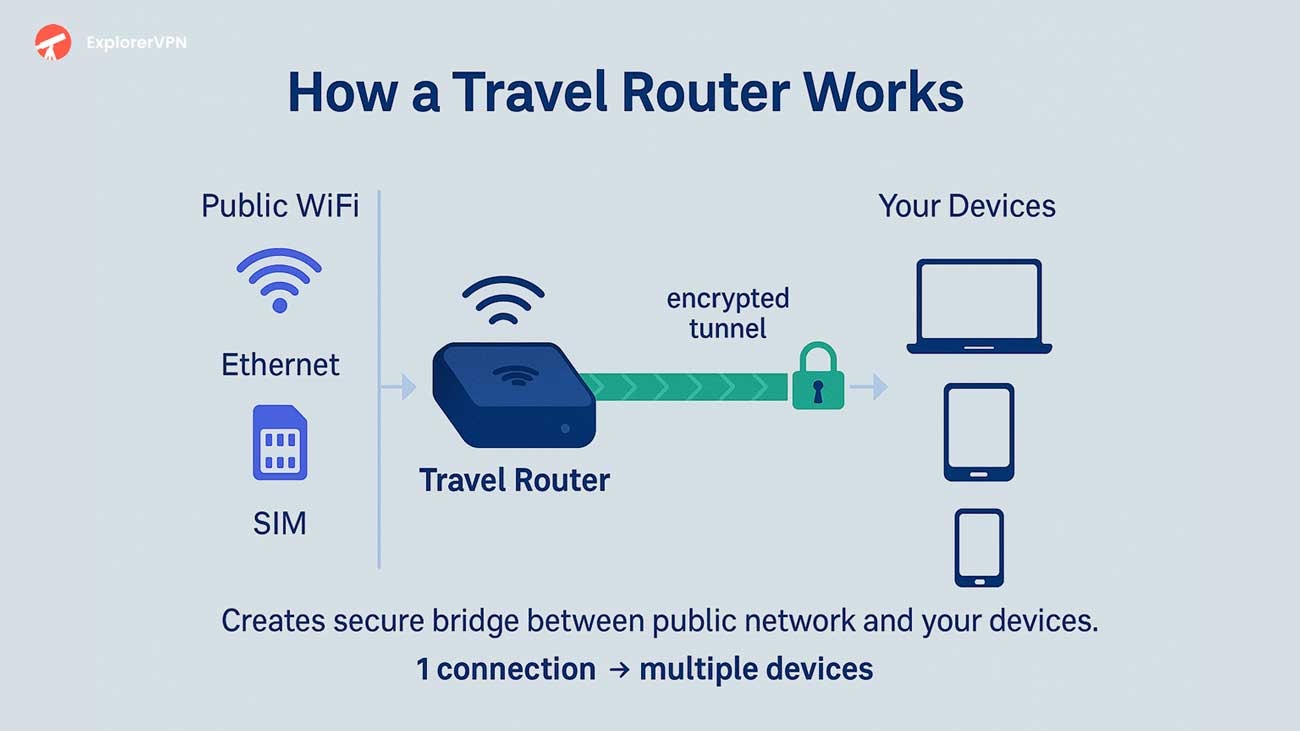
Essential Features to Look for in a Travel Router
Essential travel router features include:
-
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) dual-band support
-
Sub-200g weight with compact under-4-inch dimensions
-
Integrated 4–8 hour batteries
-
WireGuard VPN achieving 550 Mbps throughput
-
Multi-gigabit WAN ports supporting 2.5 Gbps speeds
-
USB 3.0 connectivity for NAS functionality
Wi-Fi 6 technology provides critical performance advantages in congested environments where multiple devices compete for bandwidth. The 802.11ax standard delivers superior efficiency compared to obsolete Wi-Fi 4 protocols that create security vulnerabilities and performance bottlenecks.
Physical portability specifications directly impact travel convenience. Sub-200g weight ensures minimal luggage impact, while compact dimensions under four inches fit standard carry-on restrictions. Integrated batteries providing 4–8 hours of standalone operation eliminate dependency on constant power sources during transit or remote locations. An accessible power source is still required to operate the travel router when the battery is depleted or for models without built-in batteries.
Security capabilities center on WireGuard implementation, delivering 550 Mbps throughput performance. Hardware-based encryption maintains consistent speeds across multiple connected devices without processor bottlenecks. Pre-installed VPN client support for 30+ services provides immediate privacy protection without complex configuration requirements.
Connectivity flexibility requires multi-gigabit WAN ports enabling 2.5 Gbps throughput to handle high-speed internet connections without creating router-based limitations. USB 3.0 connectivity enables NAS functionality and secure local file sharing without requiring cloud dependencies or internet connectivity for file access between devices. A USB port is also important for connecting storage devices or 4G dongles, expanding the router's versatility. An Ethernet port allows the travel router to connect to wired internet sources (such as hotels or conference centers) and share the connection wirelessly with multiple devices.
Different Modes of Operation (Router, Access Point, Repeater, Hotspot)
Modern travel routers operate in five distinct modes:
-
Router mode
-
Hotspot mode
-
Access Point (AP) mode
-
Range Extender mode
-
Client mode
Each mode is designed for specific network environments and security requirements.
Router mode establishes primary NAT/DHCP services through wired Ethernet connections, delivering comprehensive network management capabilities ideal for hotel deployments where administrators need full control over network infrastructure and device management.
Hotspot mode transforms unsecured public Wi-Fi into encrypted private networks, implementing essential security protocols that protect against common vulnerabilities found in public wireless networks. This mode is crucial for travelers accessing untrusted networks.
Access Point mode (AP mode) bridges wired infrastructure to wireless connectivity, maintaining seamless device compatibility across different network segments while allowing multiple wireless devices to connect through a single wired connection point. This mode is commonly used in hotels, college dorms, or other public settings.
Range Extender mode amplifies existing Wi-Fi signals through rebroadcast protocols, significantly improving coverage areas and signal strength in environments where the original wireless signal cannot reach effectively, enhancing overall network performance metrics.
Client mode enables secure remote network authentication while preserving essential firewall protection, allowing the router to connect to existing networks as a client device while maintaining security barriers for connected devices.
Each operational mode requires specific setup procedures through dedicated user interfaces, enabling network administrators to select optimal configurations based on available infrastructure, security threat levels, and specific deployment requirements.
How to Set Up and Use a Travel Router?
Travel router setup requires powering via USB Type-C, connecting to default SSID "GL-[model]-XYZ", accessing admin panel at 192.168.8.1, replacing default credentials, and establishing internet connectivity through Ethernet WAN, Wi-Fi repeater mode, USB tethering, or cellular modem.
The GL-Travel router uses a USB Type-C power connection and broadcasts its default SSID visible on the device label following the "GL-[model]-XYZ" format. The admin panel interface operates optimally through Chrome, Edge, or Safari browsers at the 192.168.8.1 IP address.
Security configuration involves replacing the default "admin" credentials with secure passwords and establishing custom SSID credentials to prevent unauthorized access. The router supports four internet connectivity methods: Ethernet WAN port for direct cable connection, Wi-Fi repeater mode through "Wi-Fi as WAN" selection to extend existing networks, USB tethering with smartphone hotspot functionality, and cellular modem insertion for mobile data access.
Configuration completion appears through light blue connectivity indicators in the dashboard interface, confirming successful network establishment. The systematic configuration procedures address security vulnerabilities while maintaining reliable network connectivity across different deployment scenarios and operational modes.
Ideal Use Cases and Scenarios for Travel Routers
Travel routers become critical for mobile professionals during international travel, remote work sessions, and when accessing untrusted public networks including hotel Wi-Fi, airport hotspots, and venue-restricted connections.
Network security vulnerabilities emerge when business professionals handle sensitive data on compromised public Wi-Fi infrastructure. Travel routers provide encrypted VPN tunnels and DNS filtering to prevent data exposure through malicious captive portals and man-in-the-middle attacks on hotel networks and airport connections.
Device management limitations occur when venues restrict connections per guest, forcing repeated authentication across laptops, tablets, and streaming devices. Travel routers solve this by presenting a single connection point to the network while creating a private wireless network for multiple devices simultaneously. For example, when using in flight wi fi, a travel router can share the purchased connection with your work laptop and other devices, allowing you to save money and stay connected across all your gadgets during flights.
Remote work connectivity requires stable bandwidth for video conferencing and uninterrupted business operations. Travel routers deliver failover connectivity using local SIM cards when primary internet connections fail, ensuring continuous access during critical business meetings and deadline-sensitive projects.
Geo-restricted content access, for example, but not limited to Hulu, Hotstar or Ome TV becomes essential for travelers needing access to region-locked services and applications. Travel routers with integrated VPN capabilities enable seamless access to home-country services, streaming platforms, and business applications regardless of geographic location or local internet restrictions.
Best Travel Router Models for 2025
Top travel routers for 2025 include:
-
GL-iNet GL-AXT1800 – 1800Mbps, OpenWrt VPN
-
Netgear Nighthawk M6 Pro – 2.9Gbps, 5G cellular, Wi-Fi 6E
-
GL-iNet Barrel AX – dual 2.5Gbps Ethernet, WireGuard
-
Puli AX – 5G integration, NAS functionality
Professional-grade travel routers in 2025 incorporate Wi-Fi 6 protocols, cellular failover mechanisms, and enterprise-level encryption to address connectivity vulnerabilities in critical use scenarios. Travel router comparisons reveal distinct performance tiers across deployment requirements.
The GL-iNet GL-AXT1800 delivers 1800Mbps throughput with OpenWrt-based VPN configurations, earning PC Guide’s top overall ranking for its balance of performance and customization capabilities. TP-Link’s TL-WR3002X prioritizes portability through an antenna-free design while requiring external cellular tethering for mobile connectivity.
Top-rated models like the Netgear Nighthawk M6 Pro integrate 5G cellular modems with Wi-Fi 6E tri-band support, reaching 2.9Gbps maximum speeds. GL-iNet’s Barrel AX features dual 2.5Gbps Ethernet ports with WireGuard encryption optimization for high-speed wired connections and enhanced security protocols.
The Puli AX combines 5G cellular integration with NAS functionality, targeting enterprise deployments that require thorough failover protocols and advanced security frameworks for mission-critical connectivity needs.
How to Choose the Right Travel Router for Your Needs
Key travel router selection factors include:
-
Wi-Fi 6 standards delivering 50–70% of theoretical speeds
-
Battery life of 3–10 hours
-
Device capacity ranging from 10–50+ connections
-
Dual-band frequency architecture (2.4GHz and 5GHz)
-
WPA3 security encryption
-
Coverage range of 50–150 feet
Travel router performance depends on matching processor specifications between 500MHz–1.5GHz to your concurrent device requirements. Wi-Fi 6 technology provides the most current standard, though actual throughput typically reaches only 50–70% of advertised maximum speeds in real-world conditions.
Battery-powered models offer portable internet access for 3–10 hour operational windows, making them suitable for day trips, meetings, or temporary workspace setups. Device capacity varies significantly — entry-level units support 10–20 connections, while enterprise models accommodate 30–50+ simultaneous devices. If you choose a travel router that supports SIM cards or cellular connectivity, be sure to consider your data plan needs to ensure reliable access and compatibility with your travel requirements.
Dual-band architecture using both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies provides an optimal balance between extended range and high-speed performance for most travel scenarios. The 2.4GHz band offers better wall penetration and longer range, while 5GHz delivers faster speeds with less congestion.
WPA3 encryption with 192-bit enterprise security suites ensures maximum protection for sensitive data transmission and meets current regulatory compliance standards. This security protocol provides significant improvements over older WPA2 standards.
Coverage specifications typically range from 50–150 feet, with beamforming technology enhancing signal penetration through walls and obstacles. Travel routers featuring MU-MIMO and OFDMA technologies deliver superior network efficiency when multiple devices connect simultaneously — particularly valuable in high-density environments like hotels or conference centers.
How VPN adds benefits while using travel router?
VPN integration with travel routers provides comprehensive security encryption, geo-restriction bypassing, man-in-the-middle attack prevention, and multi-device protection through a single connection point.
This security architecture encrypts all network traffic before transmission, effectively preventing Internet service providers, hotel networks, and public Wi-Fi operators from monitoring user activity or intercepting sensitive data, and protecting your data from prying eyes on public networks. The configuration mitigates man-in-the-middle attacks and credential theft risks inherent in unsecured networks commonly found in hotels, airports, and cafes.
Geo-restriction bypassing capabilities enable access to region-locked content by routing traffic through VPN servers in different countries, allowing travelers to access home streaming services, banking platforms, and restricted websites regardless of location. The architecture supports multiple VPN protocols including WireGuard, OpenVPN, and IPsec for enhanced encryption standards and connection reliability.
Multi-device protection eliminates the need for individual VPN software installations while maintaining secure browsing across smartphones, laptops, tablets, and gaming consoles simultaneously. All connected devices benefit from the same security level and geographic flexibility through the travel router’s centralized VPN connection, creating a portable secure network environment for travelers.
Most common questions about travel routers
Can Travel Routers Work With Airline Wi-Fi During Flights?
Yes, travel routers can work with airline Wi-Fi during flights by connecting through captive portal authentication systems. Travel routers successfully establish connections with airline Wi-Fi networks and enable multiple devices to share a single internet connection. However, many airlines have terms of service that specifically prohibit connection sharing between passengers, which could violate their usage policies. The performance of in-flight connectivity varies significantly depending on the satellite infrastructure provider used by the airline, with some offering faster speeds and more reliable connections than others. Passengers should check their airline's Wi-Fi policies before using travel routers to avoid potential service restrictions.
Do Travel Routers Drain Laptop or Phone Battery Faster?
Travel routers typically help conserve laptop and phone battery life compared to using mobile hotspots. Travel routers eliminate the need for phones to run power-intensive mobile hotspot functionality, which significantly reduces phone battery drain. For laptops, connecting to a travel router's WiFi network generally consumes less power than maintaining cellular data connections or other wireless protocols. However, unstable travel router connections can cause devices to cycle through WiFi scanning and reconnection processes, which increases power consumption and may drain batteries faster than stable direct connections. The overall battery impact depends on the router's connection stability, signal strength, and the specific power management capabilities of the connected devices.
Are Travel Routers Allowed Through Airport Security and Customs?
Yes, travel routers are allowed through airport security and customs. TSA airport security regulations explicitly permit travel routers in carry-on luggage without removal requirements. Most countries' customs inspection procedures classify consumer-grade routers as personal electronics, requiring no special declarations for temporary use.
Can Multiple People Share One Travel Router Simultaneously?
Yes, multiple people can share one travel router simultaneously. Travel routers enable multiple devices to establish secure connections simultaneously through WPA3 encryption protocols. Most models support 5-20 concurrent users, though performance degradation risks increase with higher device loads and bandwidth demands.
Do Travel Routers Work Internationally With Different Power Outlets?
Yes, modern travel routers work internationally with different power outlets through USB-C charging compatibility. Most 2025 travel routers feature USB-C power inputs with universal voltage compatibility (100-240V), eliminating the need for traditional travel router adapters. International power compatibility relies on standard USB-C PD (Power Delivery) protocols rather than region-specific outlets, reducing power infrastructure dependencies. This means you can power your travel router using any USB-C charger, power bank, or laptop adapter regardless of the country's electrical outlet configuration.